

Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes such topics as numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory,[2] algebra,[3] geometry,[2] and analysis,[4][5] respectively.
Physics is the natural science that studies matter,[a] its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force.[2] Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves.[b][3][4][5] A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist.
Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, composition, and structure of elements and compounds, how they can change, and the energy that is released or absorbed when they change.


Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field.[1][2][3] For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. English is genealogically West Germanic, closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages; however, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of French (about 29% of modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language).Speakers of English are called Anglophones.


Bengali generally known by its endonym Bangla (বাংলা, Bengali pronunciation: [ˈbaŋla]), is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken of the 22 scheduled languages of India. With approximately 300 million native speakers and another 37 million as second language speakers, Bengali is the fifth most-spoken native language and the seventh most spoken language by total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the fifth most spoken Indo-European language..
Hindi (Devanāgarī: हिन्दी, हिंदी, ISO: Hindī), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: मानक हिन्दी, ISO: Mānak Hindī),[9] is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register[10] of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English.. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India


History (from Ancient Greek ἱστορία (historía) 'inquiry; knowledge acquired by investigation')[1] is the study and the documentation of the past.[2][3] Events before the invention of writing systems are considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers.[4]
Geography (from Greek: γεωγραφία, geographia, literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.[1] The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC).[1] Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth
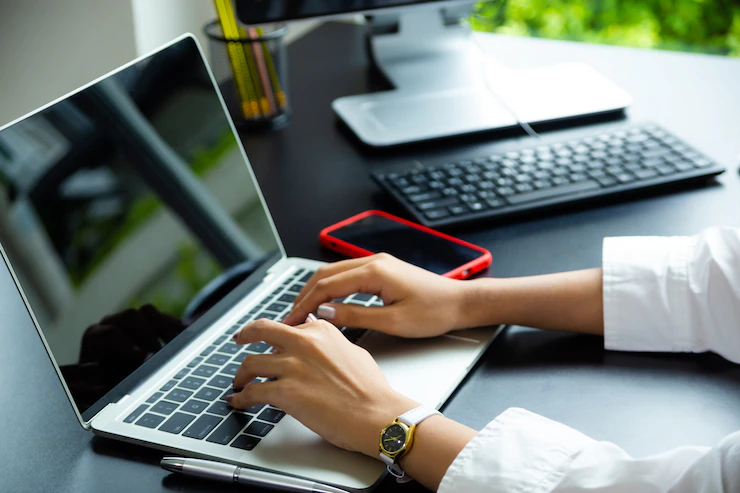


A computer is a digital electronic machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a "complete" computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for "full" operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster.